A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood supply to a certain part of the brain is disrupted due to a blockage or rupture in any of the brain’s arteries. Interruption in blood flow causes an interruption in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the pertinent brain area. Early intervention plays a major role, whereby it reduces a patients’ brain damage and saves them from complications. Assessment of the condition is therefore vital. Scale and scoring systems can help understand the patient’s condition before, during, and after treatment.
According to American Heart Association, scoring systems and scale play a major role in research and clinical practice through assessing the impact of therapeutic interventions, helping in improving diagnostic accuracy, finding out and following the clinical pathway, etc. As the “one size fits all” approach does not fit in stroke evaluation and treatment, a more accurate tool is necessary. The NIH stroke scale is an acute stroke assessment scale.
The NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a diagnostic tool that is widely used to assess stroke-related neurologic deficit and stroke severity. Initially, it was designed as a research tool for the clinical assessment of stroke patients in acute stroke clinical trials. Now it is used to determine patient condition, outcome and to plan treatment. Generally, the scale is accurate and tends to predict damage/outcomes well. In this post, we will give you an overview of the scale, how it works, what it means, and how to read it.
What is the NIH Stroke Scale?
NIHSS is an acute assessment scale, it is a commonly used tool that helps you understand the stroke’s cognitive effects on your patients. In addition, it tells you how much neurological deficit or damage has occurred due to the stroke.
It also helps create a common language between all caregivers involved in a stroke patient’s treatment. In a treatment setting, the scale has three major purposes:
- It evaluates the severity of the stroke
- It helps determine the appropriate treatment
- It predicts patient outcomes.
How is NIHSS used?
The scale has eleven components to evaluate a specific ability. Each component has a score range from 0 to 4 where 0 signifies normal functioning and 4 signifies being completely impaired. After you complete assessing all the components, you add them up to get a total score: 42 is the highest score possible. In the NIHSS, the higher the score, the more impaired a stroke patient is.
It works by assessing the following components: level of consciousness, asking age and month, asking to blink eyes and squeeze hands, assessing horizontal extraocular movements, assessing visual fields and facial palsy, assessing left and right arm motor drift, assessing right and left leg motor drift, limb ataxia, sensation, language aphasia, dysarthria, and extinction/inattention.
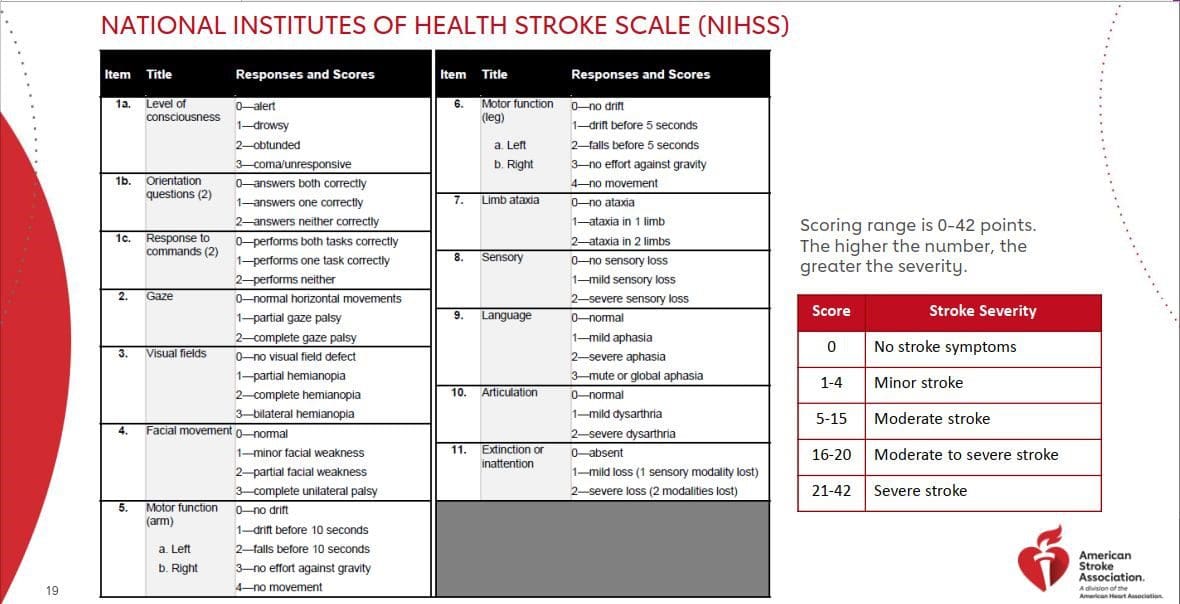
The scoring range is 0-42 points. The greater the number, the higher the severity.
- 0 means no stroke symptoms – no action required.
- 1-4 means minor stroke – take actions to prevent stroke, try to get a rapid evaluation from a doctor within 12 hours of the onset of symptoms and get all the diagnostic imaging (investigations) done. Take action to control diabetes, cholesterol, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, etc.
- 5-15 means moderate stroke – get all the investigations done, be ready for surgery.
- 16-20 means moderate to severe stroke- get to the emergency department immediately, and be ready for the surgery (carotid endarterectomy or endovascular therapy).
- 21-42 means severe stroke- get to the emergency department immediately, and be ready for the surgery.
How well does the NIHSS predict patient outcomes?
Research suggests that NIHSS gives accurate results, except in cases where the stroke was isolated to the cortex area of the brain. As per the rule, a score above 16 indicates a high risk of the patient’s death, whereas a score of 6 or lower indicates less severity and a high probability of positive outcomes. Each 1-point increase on the scale lowers the possibility of a positive outcome for the patient by 17 percent. Moreover, an increase in score has been shown to correlate with the infarction seen on CT scans and MRIs.
Why the NIHSS is score important for patients?
NIHSS is an important assessment tool because it helps you to determine the right treatment for your patients. As a health care professional, you should apply this scale soon after the onset of the symptoms—which would typically be in the emergency department of a hospital. In case the condition of the patient changes, you will need to periodically reassess the patient’s progress. In addition, it can help you to determine the short and long-term outcomes of your stroke patients.
Case Scenario:
Mr. John is a 60-year-old male and has come to the emergency department. He is diagnosed as having a stroke. He is not alert but arouses to minor stimulation (+1). On asking month and age he does not answer both questions (+2), he blinks his eyes (+1) but he is unable to squeeze his hands. Horizontal extraocular movements are assessed by asking him to follow a pen using eyeball movement which he is unable to perform at this moment (+1). There is no visual loss (0), there is unilateral complete paralysis (upper/lower face) (+3) , some effort against gravity while assessing right (+2) and left arm motor drift (+2), and some effort against gravity while assessing right (+2) and left leg motor drift (+2), Ataxia in both limbs (+2), mild to moderate loss of sensation (can feel touch) (+1), mild to moderate aphasia(+1), mild to moderate dysarthria- slurring but can be understood ( +1), and visual/ tactile/ auditory/ spatial/ personal inattention (+1).
Result: 22 points
Action
The patient needs a neurology consult. He must be evaluated for eligibility to receive the intravenous thrombolytic (as he may be a potential candidate). Find out when the stroke symptoms started, consider further investigations such as CT, CT angiography, or MRI. As a nurse, let the patient family/attendant know that these investigations are important. Provide therapeutic communication and follow nursing guidelines for the ordered medications.
Early assessment can lead to early interventions that can save the patients life. The NIH Stroke Scale is an effective tool in providing high quality patient care. Subscribe to our newsletter and check out our blog for more nursing content.